The only thing that can be guaranteed is a lack of certainty. You never know what your data center is going to throw at it, whether it be sudden power outages or intense storms. In the event that anything unexpected takes place, the environment of your data center will benefit immensely from having a strategy for redundant systems.
What exactly does “redundancy” in a data center mean?
The term “redundancy” refers to the architecture of a system in which a component is replicated in order to protect IT equipment from being affected in the event that the original component fails. For instance, having backup power sources in case there is a disruption in the primary supply. The main goal of redundancy is to make sure that there will never be any downtime, even if things go wrong.
Why is it vital to have redundancy in data centers?
Because there is less tolerance for their operations encountering any kind of downtime, most businesses are finding it more difficult to maintain their previous levels of maximum acceptable period of disruption (MTPD) tolerance. Businesses are under more pressure and are getting more requests to be able to keep running and get back up and running faster after an interruption, no matter what caused it.
There are many different aspects that go into making sure data is protected and secure. One of those essential components is ensuring that the environment of your data center has a redundancy architecture that has been carefully developed and is in place. System failures may have a major and immediate effect on the financial line of an organization, as well as on the business operations and customer experience of that company. This can result in devastating revenue loss, missed business opportunities, and a damaged reputation. The Information Technology Industry Council (ITIC) conducts a poll every year, and the results of the year 2021 poll indicate that 98 percent of firms estimate that the cost of a single hour of downtime is more than $100,000. When your employees are preoccupied with feverishly attempting to restore systems and data instead of concentrating on other primary focus areas for your company, downtime may have a significant effect on the productivity of your workforce. This impact goes beyond the monetary cost to your company.
The terms “data backup” and “data redundancy” are often used in conjunction with one another within the lexicon of data centers. There is a huge gap between the two in terms of the advantages that they deliver, despite the fact that they both help secure your data.
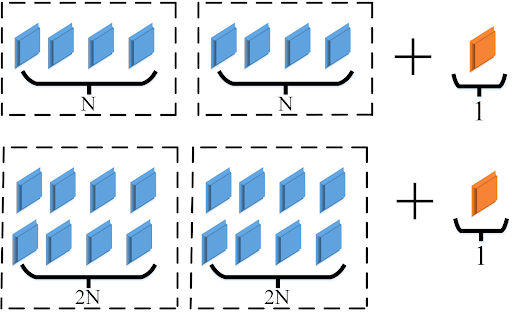
The term “data contingency,” which may sometimes be used interchangeably with the term “data replication,” refers to a component of a contingency plan, whereas the term “data backup” refers to the contingency plan itself. To explain this in layman’s words, data backup is the process of keeping copies of your data either digitally or locally, while data redundancy is the process of adding an additional layer of security to the backup in order to strengthen it. Figure 1 explains the idea of adding an extra layer of security, as well as the notions of 2N and N+1.
Figure 1: Demonstration of 2N and N+1
What’s the big deal about using 2N instead of just N+1? The question now is, what exactly is the difference between 2N and N+1? At first look, it could seem like an algebra equation, and in all honesty, it is an equation, although a very simple one. But first, you have to have a grasp of what the letter N stands for. Let’s analyze it in more detail.
Definition of N:
It doesn’t matter whether it’s a generator, UPS, or cooling unit; the word “N” simply refers to the component that you want to replicate in its entirety.
N is equivalent to the amount of capacity needed to power, backup, or cool a facility while it is operating at its maximum IT load. A design of N indicates that the facility was intended just to take into consideration the facility while it was operating at its maximum capacity, with no further redundancy included. Mission-critical applications are likely to experience downtime in the event that the data center facility is operating at full capacity and a component fails or requires repair.
You Might Also Like to Read: Tips for Picking the Best Colo Data Center For Your Business
Definition of N+1
N+1 is defined as an extra component added to support a single failure or necessary maintenance on a component. If N matches the amount of capacity required to operate the facility, then N+1 signifies an additional component that has been added. Generally speaking, design guidelines need one additional unit for every four that are required. Therefore, if you have eight UPS units, you really want to have a minimum of ten UPS units in total.
Definition of 2N
A 2N system is a completely redundant, mirrored system with two separate distribution systems. They are not related to one another in any way, nor are they dependent on one another in any way. This indicates that even if one power source encounters an interruption or loss of power, the other should still be able to deliver power and handle a full load, thereby lowering the likelihood of any possible downtime brought on by the loss of one side of the system.
It is recommended that companies provide an extra layer of security to the sensitive, customer and company data that they maintain. The fact that harmful cyberattacks may be launched against data centers may come as a bit of a surprise, particularly with regard to locally stored information. As a direct consequence of this, your backup is compromised. As a result, the primary database of the company is also affected, which puts the continued existence of the whole firm in jeopardy.
Large amounts of data are handled on a daily basis by businesses and their customers alike. It’s possible that duplicating all of this data would be detrimental in the sense that buying a larger data center to house the massive data sets would simply serve to make the system less scalable. After a certain point in time, the expense of copying the data will become unsustainable for the customers. To put it simply, it is not the case at all. Scalability is improved by having many redundant data centers.
Data centers with redundant storage are constantly evolving while also expanding their capacities. The infrastructure was built according to utilization in order to permit the delivery of exceptional service at a reasonable cost. A redundant data center is designed to accommodate change and expansion while simultaneously replicating data in a manner that is easy to manage and adaptable to changing needs. If you want to make sure that data replication goes smoothly, reliably, and quickly, your database setup must be scalable.
There are a lot of other factors that somebody might consider when choosing a data center. A few of them are given below:
Maximize availability
Your company benefits from maximum availability due to the dependability of its data center. Your main servers might cease working properly due to a variety of typical difficulties, such as a malfunctioning piece of hardware, an issue with the network, or an error in an application. Because of this, both your company and your customers could be unable to use your services. When anything goes wrong, there must be a team of trained experts and operational procedures ready to step in and take charge of the situation. In the case of a crisis that hinders performance, your servers will continue to operate normally, and the load may be shifted between them as necessary. In the case of a crisis that hinders performance, your servers will continue to operate normally, and the load may be shifted between them as necessary.
Preserving sensitive information
Preserving essential data is one of the most crucial ways in which redundancy in your data center directly benefits your company. The data that you store on your servers and drives is susceptible to being corrupted, experiencing hardware difficulties, or even being accessed by malicious users. The presence of redundancies guarantees that your essential data is stored in more than one location. There are backups stored off-site in addition to the drives that are redundant in the data center. Because of these backups, you will be able to get your data back if something happens to your servers or hard drives. This will help your company get back to business quickly.
You Might Also Like to Read: Affordable UK Colocation – Best Provider of 2022
Enhanced protection for the server
Hackers may use a wide variety of strategies to launch attacks on your servers and perhaps obtain access to confidential or private information. In today’s world, this is a common occurrence. The greater safety of servers is one benefit that may be gained by using redundant data centers. Your information will remain secure due to the redundant systems. Hackers won’t be able to exploit the vulnerabilities that might arise during or after a server breakdown thanks to these protections. In addition, redundancies make it impossible for some kinds of assaults to succeed in any way. In addition, redundancies make it impossible for some kinds of assaults to succeed in any way.
Become less difficult to upgrade
There will come a moment when you will be required to do an update on your servers as well as other components of your infrastructure. In a conventional configuration, it is customary to take all of the systems down and halt routine business activities. You will be able to update without having to entirely cease conducting business if your data center is reliable, which is one of the advantages of having reliable data storage. This means you can keep working and taking care of clients while the procedure is done.
For Discount and Offers, Visit our Official Twitter Page